
Audio Drivers and Performance
How to Select the Audio Driver
Sound Mill allows for use of two different audio drivers:
-
 Media Player (MP) driver
Media Player (MP) driver -
 Windows Audio (WA) driver
Windows Audio (WA) driver
Each Sound Item can use either driver based on your sound requirements.
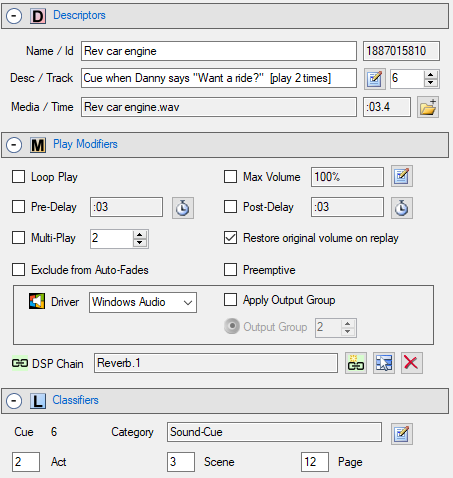
To select the audio driver for a given Sound Item, use the Driver pulldown menu on the Play Modifiers panel (Figure 2).
Audio Driver Selection Recommendation
Each driver has its own advantages and limitations. Here's how to pick the right driver for your requirement.
General Rule of Thumb
- The Media Player (MP) driver is the Preferred driver in most cases. The MP driver supports more audio formats than the WA driver. However, since it does not support Output Groups, the audio can only be played on one speaker system -- the Default Windows Playback device selected in the Windows Control Panel > Sound settings.
- Use Windows Audio (WA) driver: 1) to play audio to multiple speaker systems. This is accomplished via Output Groups; 2) if your source audio is web-based HTTPS (secure HTTP); 3) if you want to use DSP Effects.
- Video File Formats - Both drivers will play the audio portion of a video file (ex. MP4, WMV, and more). As mentioned the MP driver will support more formats than the WA driver.
About Media Player Driver

The Media Player(MP) Driver is the Microsoft .Net audio driver. As such, it has a much larger development team (Microsoft) than the WA driver (open source).
- Audio Formats - It can support a wide variety of audio formats without any added Codec packages. See the full list of supported audio formats. Installing a codec package will expand the number of supported formats (see K-Lite section below).
- Output to One Soundcard - MP Driver will play sound ONLY to the Windows Default Playback Device selected in the Windows Control Panel.
- Codecs - With an additional codec package installed, you can greatly extend the number of supported audio formats.
- Web Based Media (HTTP) - If you plan to play web streaming media, this driver supports HTTP, but NOT HTTPS (secure HTTP).
- No DSP Effects - DSP Effects are not available.
About Windows Audio Driver

The Windows Audio (WA) Driver is based on an open source audio library (NAudio) which uses the the Windows Audio Session API (WASAPI). It provides a few key features not available with the Media Player Driver.
- Audio Formats - It supports many audio formats: WAV, MP3, WMA, FLAC (and more). Also the audio portion of some video formats (MP4, WMV, AVI etc) will play. Installing a codec package will expand the number of supported formats (see K-Lite section below). With this driver, there is no guarentee that all the K-Lite media formats will work. MIDI is not supported.
- Output to Multiple Soundcards - It has the capability of directing audio output to one or multiple soundcards simultaneously (via the Output Groups feature ).
- Web Based Media (HTTP and HTTPS) - If you plan to play web streaming media, this driver supports both HTTP and HTTPS (secure HTTP).
- DSP Effects - DSP Effects are available.
- Old Audio Files - Some very old audio files may not play with this WA driver. Formats like WAV, MP3, etc have undergone multiple revisions over the years and this driver may not support older versions. Try running the audio file through a modern converter program to reformat the file.
- Hardware Supported - In general, if the device's output(s) are listed in the Windows Control Panel > Sound > Playback tab, it should be accessible to Windows Audio Driver. If the output ports are not showing up there, the device may need a device driver update. Check the manufacturer's website to see if there is a driver update to support Microsoft Windows Audio Session API (WASAPI). Also, remember that the device must have a device driver that supports your target Operating System (10,8/7).
Latency
Latency can tune the Windows Audio Driver for optimum performance. The Latency Default Value (100 ms) should work well on the majority of systems. You set the default Latency in the Options > General dialog (Audio Output Drivers settings). The best setting is really based on the speed of your system hardware components. Windows Audio Driver uses data buffers to process audio and Latency determines the size of the buffers. If you experience jittery, choppy sound or clicks, the Latency setting may be too low causing dropouts.
Tech Note: Windows Audio Driver uses the open source NAudio library.
Using Codecs to Add More Audio Formats (K-Lite Codec)
We have tested the FREE K-Lite Codec Pack download which works fine and has an expansive list of supported audio and video file types. We have never had a problem with K-Lite and it adds a lot of media type functionality including the latest High Def video formats. The codec quality is very good.
K-Lite supported formats: Here is a Comparison table showing the audio and video file formats supported by the different variants of the K-Lite Codec Pack. Install the variant that supports the filetypes that you need.
Recommendations
- Create a Windows System Restore Point prior to installing this package. It installs a lot of codecs if you accept the default install. Test all your audio and video apps after installing. If you find something is not working, restoring back to the Restore Point you created may be a cleaner option than uninstalling the codec package.
- There is a Step in the install that asks if you want to create filetype associations with Windows Media Player, Media Player Classic (which comes with the Codec), or no associations. Think about which player you want to use most often before making this choice.
- There are 4 variants of the K-Lite Codecs. Make sure the variants that supports the audio/video/file formats you need. The Full pack is recommended for the most coverage.
 Page Bottom
Page Bottom To Page Top
To Page Top